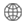
· Magnafolate® no need metabolism, can be absorbed directly
while food folate and folic acid need to undergo several biochemical conversions in the body to become L-5-MTHF.
 Español
Español Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türkçe
Türkçe  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  العربية
العربية  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan  Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski  मराठी
मराठी  Srpski језик
X
Srpski језик
X

For almost 20 years, we have become the most professional manufacturer in the world, No.1 in China in the methylfolate industry. With strict quality guarantee system, strong brand awareness and high-level after sale service, our company is famous for the business philosophy “Only manufacture and supply premium quality products.”

· Magnafolate® no need metabolism, can be absorbed directly
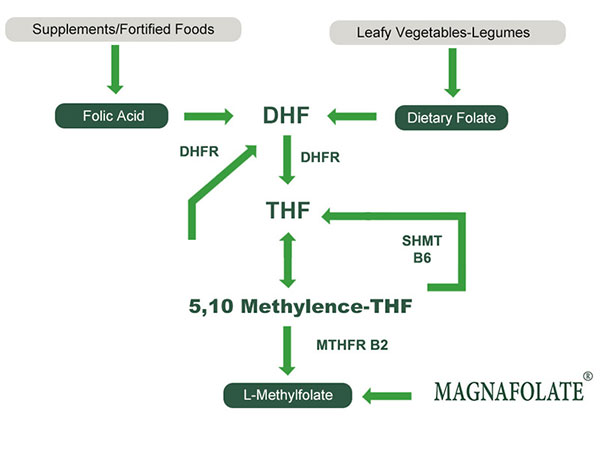
· What is MTHFR 677 TT gene mutation?
· Global MTHFR polymorphism distribution
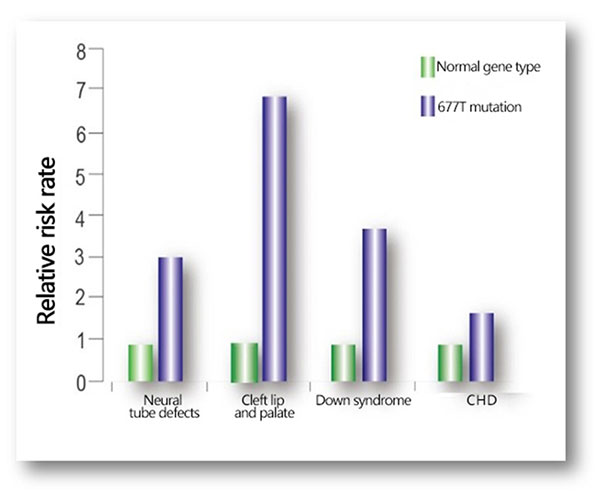
· MTHFR polymorphism complications
· Potential Dangers of Folic Acid
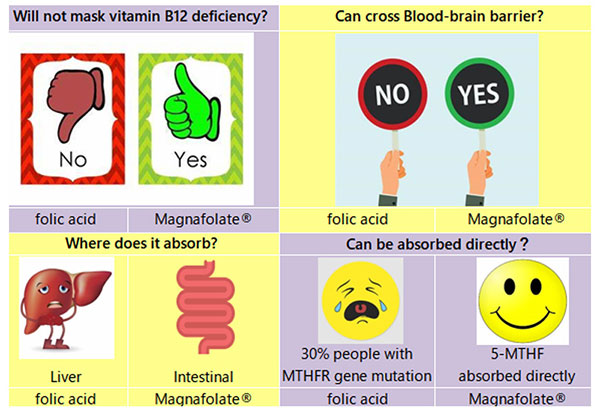
· Quick Summary
Acute toxicity |
N/A |
LD50 10mg/kg |
LD50 2000mg/kg |
MTD>15g/kg |
Cover up the use of VB12 ? |
No |
Yes |
No |
No |
Can it across into the brain? |
Yes |
NO |
Yes |
Yes |
Absorption site |
Through the intestinal absorption, do not need to go through the liver, the dosage is unlimited |
Liver, the dosage is limited |
Through the intestinal absorption, do not need to go through the liver, the dosage is unlimited |
Through the intestinal absorption, do not need to go through the liver, the dosage is unlimited |
Absorption and utilization |
After hydrolysis |
Need three step enzyme catalysis |
Directly |
|
Genetic abnormality |
Effective |
Inefficient |
Effective |
|
Source |
Difficult to obtain |
The easiest to obtain |
Easy to obtain |
|
Cost |
High cost |
The lowest cost |
Lower cost |
|
Chemical stability |
Extreme unstable |
Stable |
Stable |
|
Reducibility |
Strong |
N/A |
Strong |
|
Dosage |
High limit |
High limit |
Low limit |
|
Side effect |
N/A |
Causes a decrease in immunity multiple births, leukemia, arthritis, and certain diseases that have not yet been found |
N/A |
|
Effects on the liver |
Protects the liver by protecting GSH activity, but is less affected by fewer amounts |
Increase liver burden |
Protects liver by protecting GSH activity |
|

Copyright © 2021 Lianyungang Jinkang Hexin Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd. All Rights Reserved jinkang-chem
 Online Service
Online Service