
This poses as a problem for folic acid supplementation, as it has been found that in people with this type of polymorphism, folic acid is unable to raise plasma L-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate levels. Calcium salt of L-5 Methyltetrahydrofolate has a great stability profile and it has been shown to be a superior supplement to folic acid as it reduces the potential for masking haematological symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency (Savage & Lindenbaum, 1994), reduces interactions with drugs that inhibit dihydrofolate reductase and overcomes metabolic defects caused by methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase polymorphism, as well as reducing the potential negative effects of folic acid in peripheral circulation.
Magnafolate L Methylfolate raw material
Magnafolate L Methylfolate ingredient
 Español
Español Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türkçe
Türkçe  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  العربية
العربية  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan  Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski  मराठी
मराठी  Srpski језик
Srpski језик 
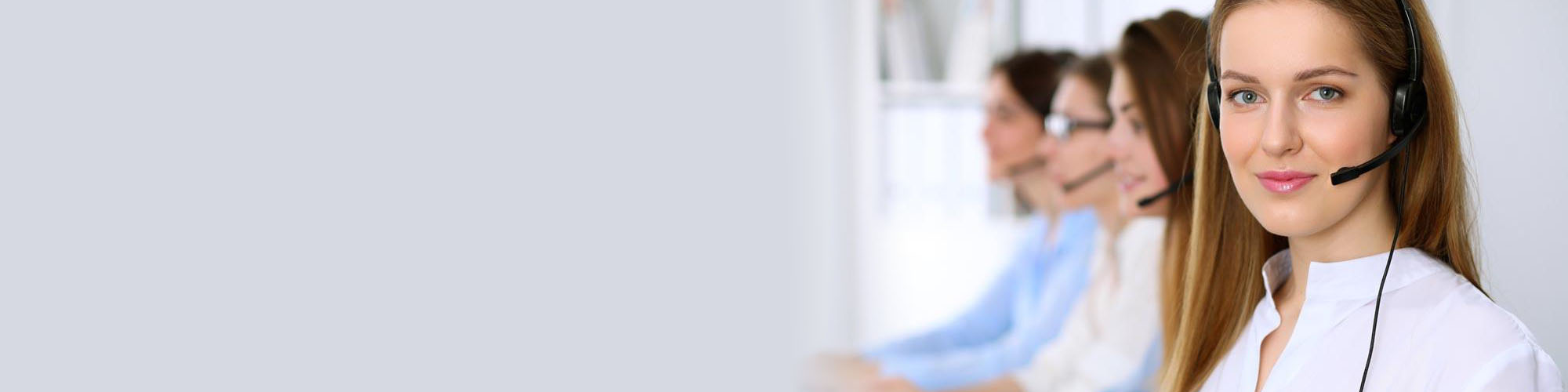








 Online Service
Online Service