
The main metabolic history of inactive synthetic folic acid in the body is as follows: during absorption in the intestine and during transport to peripheral tissues, synthetic folic acid is reduced by dihydrofolate reductase to dihydrofolate; dihydrofolate continues to be reduced by dihydrofolate reductase to tetrahydrofolate: tetrahydrofolate is then converted to 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate; 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate is finally reduced by methylenetetrahydrofolate 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate is finally catalyzed by methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) to form L-5-methyltetrahydrofolate, which is involved in two key metabolic pathways: methylation processes and DNA synthesis. It is through these metabolic processes that inactive synthetic folic acid is converted into biologically active 5-methyltetrahydrofolate.

Therefore we recommend calcium L-5-methyltetrahydrofolate:
Magnafolate is the unique patent protected C crystalline L-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate Calcium salt (L-5-MTHF Ca) which can get the purest and most stable bio-active folate.
Magnafolate can be absorbed directly, no metabolism, applied for all people.
 Español
Español Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türkçe
Türkçe  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  العربية
العربية  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan  Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski  मराठी
मराठी  Srpski језик
Srpski језик 
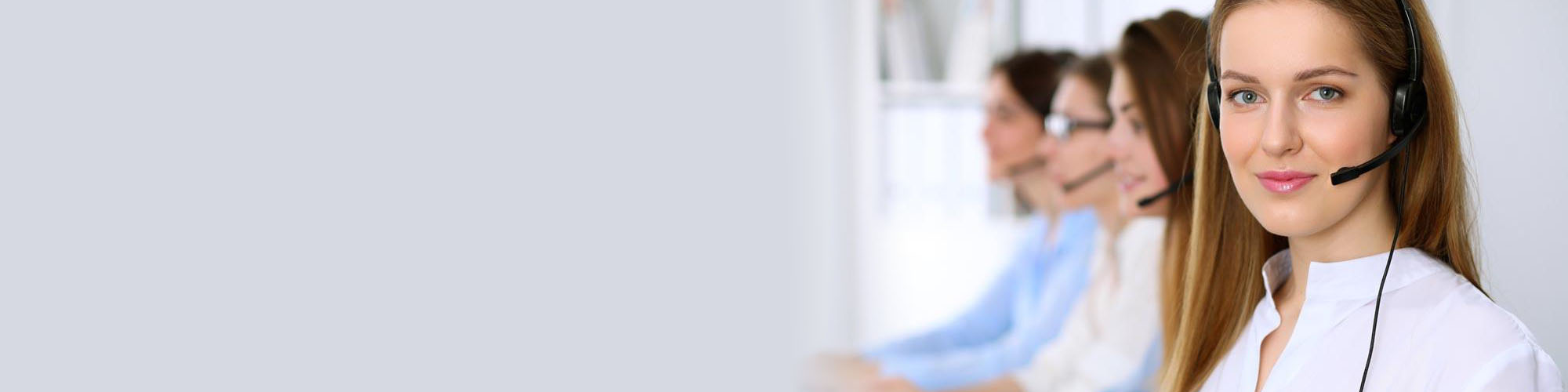








 Online Service
Online Service