Introduction: In the realm of functional foods and nutritional fortifiers, the quest for efficient, stable, and safe nutrients is critical. Magnafolate (6S-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate Calcium Form C Crystal), a novel active folate, is gaining industry attention for its biological activity and stability. Yet, challenges remain in practical applications, such as impacts of temperature, pH, and light on its stability.

I. Characterization of Magnafolate:
The 2024 study published in "LWT - Food Science and Technology" conducted an in-depth analysis of Magnafolate's properties, stability, and its synergistic stabilization with Ascorbic Acid (AA) and Cysteine (Cys). This comprehensive evaluation provides a solid scientific foundation for the practical application of Magnafolate in the food industry.

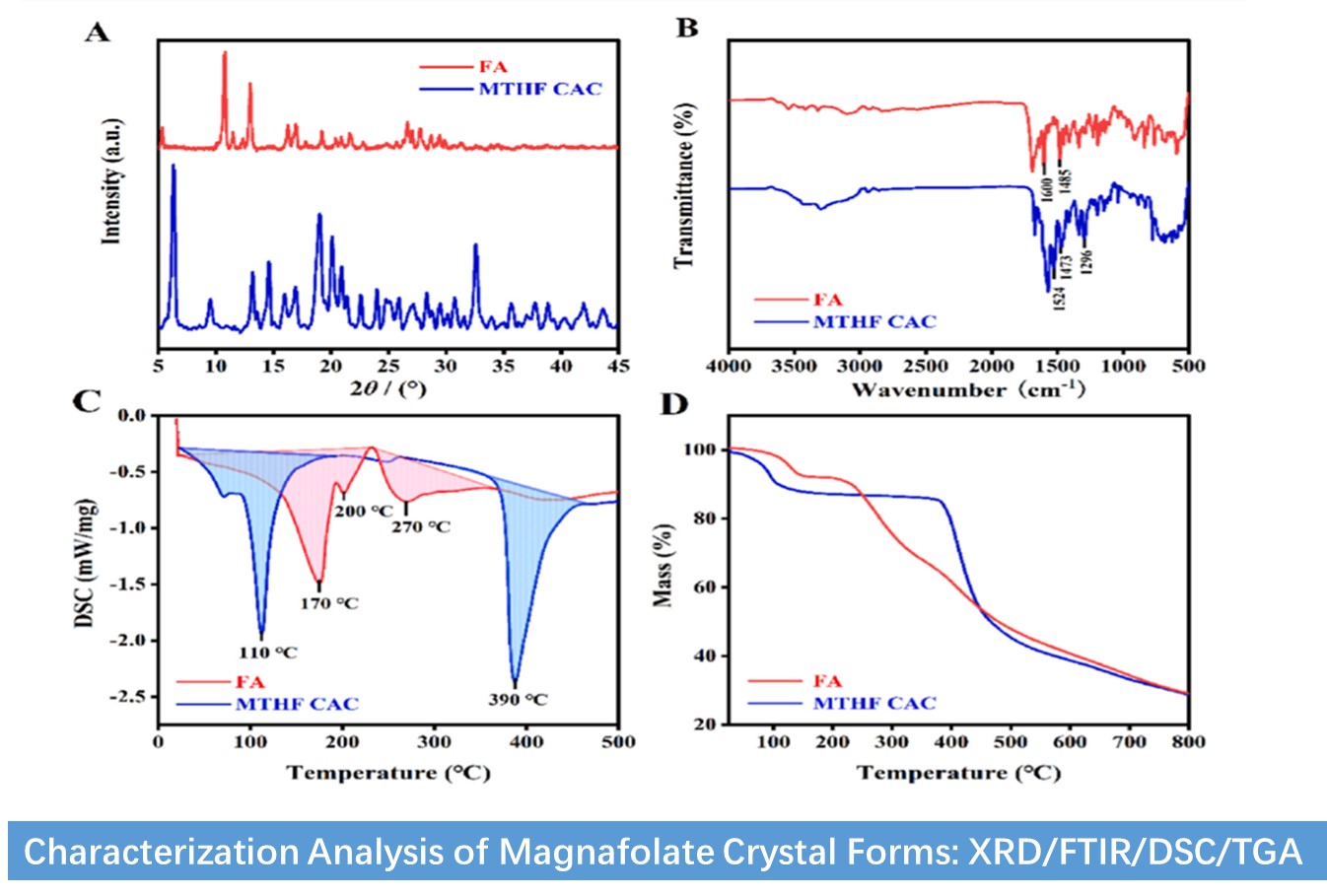
The study used advanced methods to comprehensively characterize Magnafolate's crystal and thermal stability:
X-ray Diffraction (XRD): XRD scans showed Magnafolate's crystallinity at 96.8%, slightly higher than synthetic folic acid's 96.6%, indicating highly ordered molecular chains and high stability.
Fourier-transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR): FTIR analysis confirmed key functional groups in Magnafolate's structure, solidifying the understanding of its chemical nature.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) & Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA): DSC and TGA pinpointed Magnafolate's decomposition temperature at ~390°C, markedly higher than synthetic folic acid's ~270°C, highlighting its impressive high-temperature stability.
II. Stability Influencing Factors:
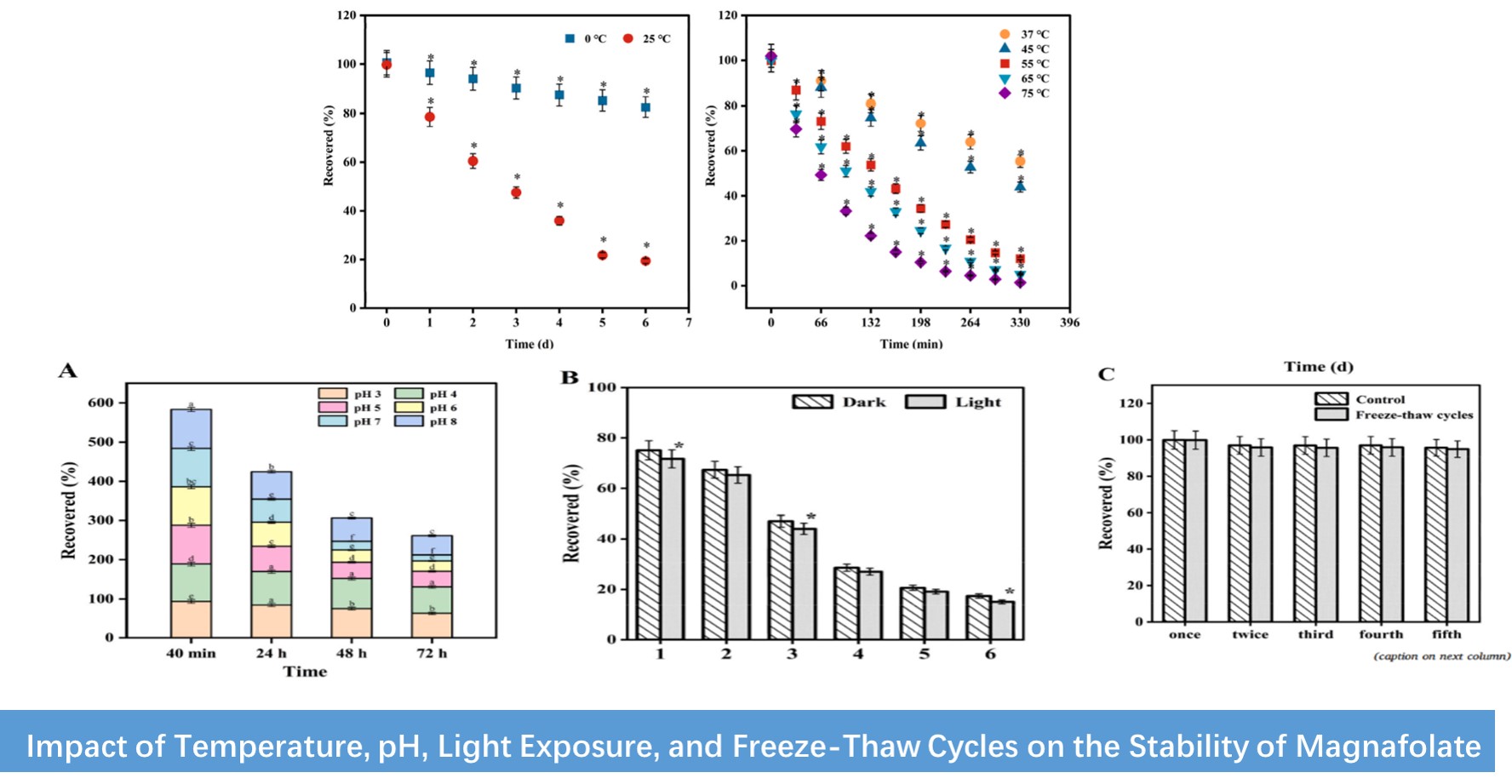
Stability is not a constant attribute. Utilizing High-performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), the study meticulously evaluated the impact of varying temperatures, pH levels, light exposure, and freeze-thaw cycles on Magnafolate's stability:
· Temperature Impact: Temperature plays a significant role in Magnafolate solution retention. At a low temperature of 4°C, the retention rate after six days was 82.6%, whereas at a high temperature of 75°C, the retention rate plummeted to 0.8% within just 330 minutes. This indicates that high temperatures are detrimental to Magnafolate's storage.
· pH Impact: The pH level is a critical factor. Magnafolate exhibits enhanced stability under acidic conditions (pH 3-4), with a notable decrease in stability observed under neutral and alkaline conditions.
· Light Impact: Light exposure accelerates the degradation of Magnafolate. However, storing it away from light can substantially improve its retention rate.
· Freeze-thaw Cycle Impact: Freeze-thaw cycles have a relatively minor effect on Magnafolate. After five cycles, the retention rate was still maintained at 94.9%.
III. Stability Protection Methods:
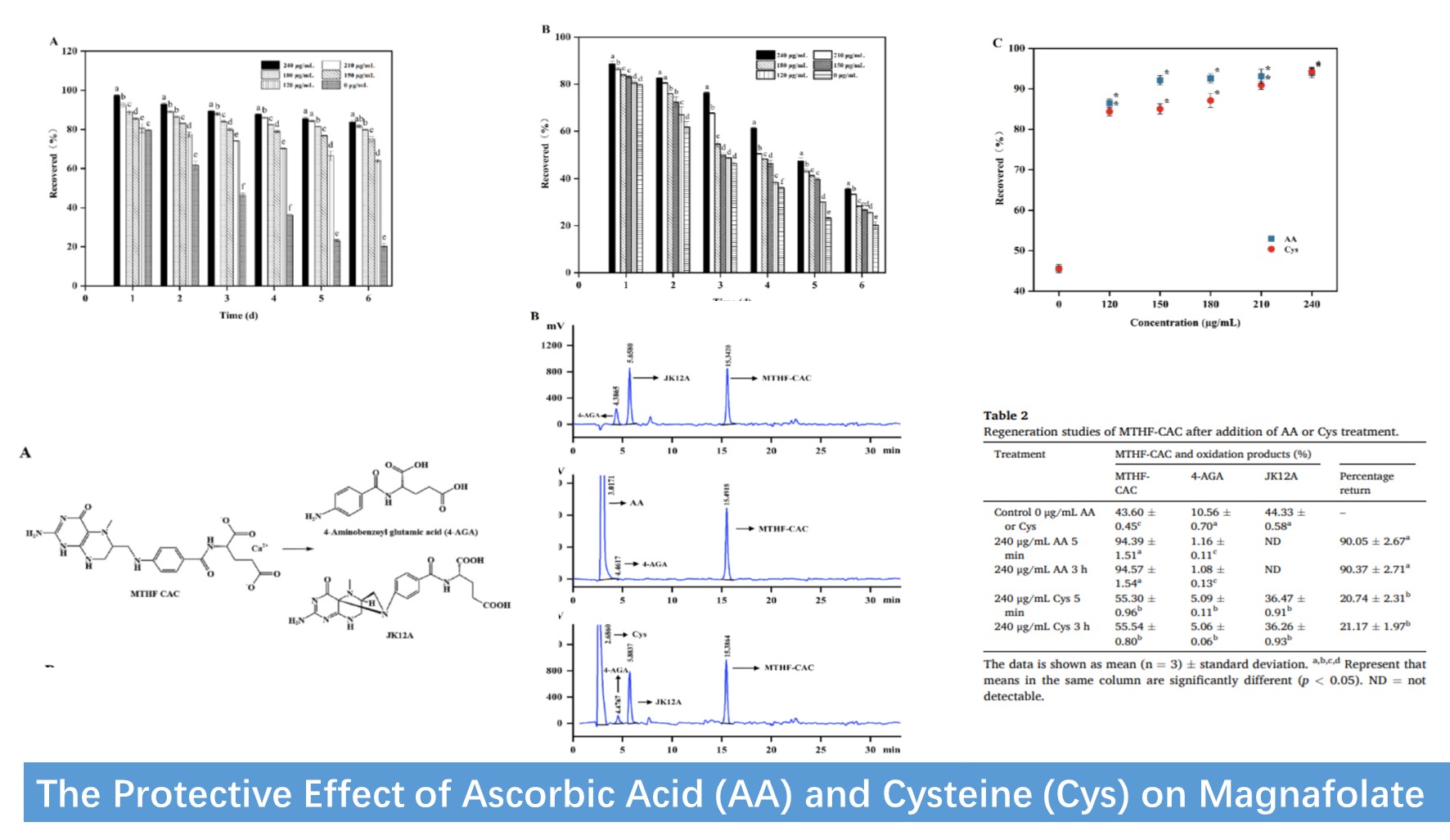
Exploring stability protection, the study found that Ascorbic acid (AA) and Cysteine (Cys) significantly protected Magnafolate under Ultra-high Temperature (UHT) conditions.
Vitamin C (AA): 120 μg/mL of Vitamin C improved Magnafolate retention by 89.9%, slightly surpassing Cysteine's effect.
Cysteine (Cys): Cysteine also boosted retention to 85.3%.
Excitingly, these protectants not only safeguard Magnafolate's stability but also regenerate it post-heat oxidation. Vitamin C achieved a regeneration rate of 90.1%, while Cysteine reached 20.7%, opening possibilities for Magnafolate "regeneration."
IV. Application Outlook for Magnafolate:
Magnafolate, with its superior biological activity and stability, is poised to make significant strides in functional foods and nutritional fortifiers. This study, through rigorous experiments and in-depth data analysis, has explored Magnafolate's stability across diverse conditions and proposed effective protection strategies, particularly leveraging the synergistic effects of Vitamin C and Cysteine. These findings provide a robust scientific foundation for its application in the food industry.
A key highlight is Magnafolate's status as the world's only Naturalization folate-certified active folate. Its production process is meticulously designed to avoid toxic substances like Formaldehyde and p-Toluenesulfonic acid, with stringent control over harmful impurities such as JK12A and 5-Methyltetrahydropteroic acid. This commitment to safety ensures near non-toxic levels, making it an optimal choice for pregnant women and infants. It rapidly elevates serum and red blood cell folate levels, thereby safeguarding maternal and infant health.
As food technology continues to advance, Magnafolate is set to play an increasingly pivotal role in promoting healthy diets. Looking ahead, we envision its expanded application across various sectors, where it will not only drive innovation but also deliver substantial value to the industry.

Reference:
Xu T, Wang K, Zhang J, et al. Study on the Characterization of 6S-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate Calcium Salt Crystal Form C and its Stability Improvement by Ascorbic Acid and Cysteine. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 2024, 198: 115984.
 Español
Español Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türkçe
Türkçe  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  العربية
العربية  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan  Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski  मराठी
मराठी  Srpski језик
Srpski језик 








 Online Service
Online Service