Folate supplementation during pregnancy has always been a crucial topic in prenatal care, as it directly impacts the health of both the fetus and the expectant mother. Today, we will delve into a study on naturalized folate (L-5-methyltetrahydrofolate calcium, L-5-MTHF-Ca) and its role in folate supplementation for pregnant women, exploring why it is becoming a new choice for folate supplementation during pregnancy.

Why is Folate Supplementation Important during Pregnancy?
Folate, a water - soluble vitamin B9, is vital for fetal neural tube development. Folate deficiency in early pregnancy may lead to neural tube defects and congenital heart diseases in fetuses. Moreover, folate promotes overall fetal growth, prevents anemia during pregnancy, and regulates maternal mood. However, the human body cannot synthesize folate on its own, and the requirement for folate increases significantly during pregnancy.

Inadequate folate intake during the periconceptional period can heighten the risk of congenital heart disease in offspring. In contrast, boosting maternal RBC folate levels can effectively mitigate this risk. RBC folate levels are a key indicator of long - term folate status in the body.
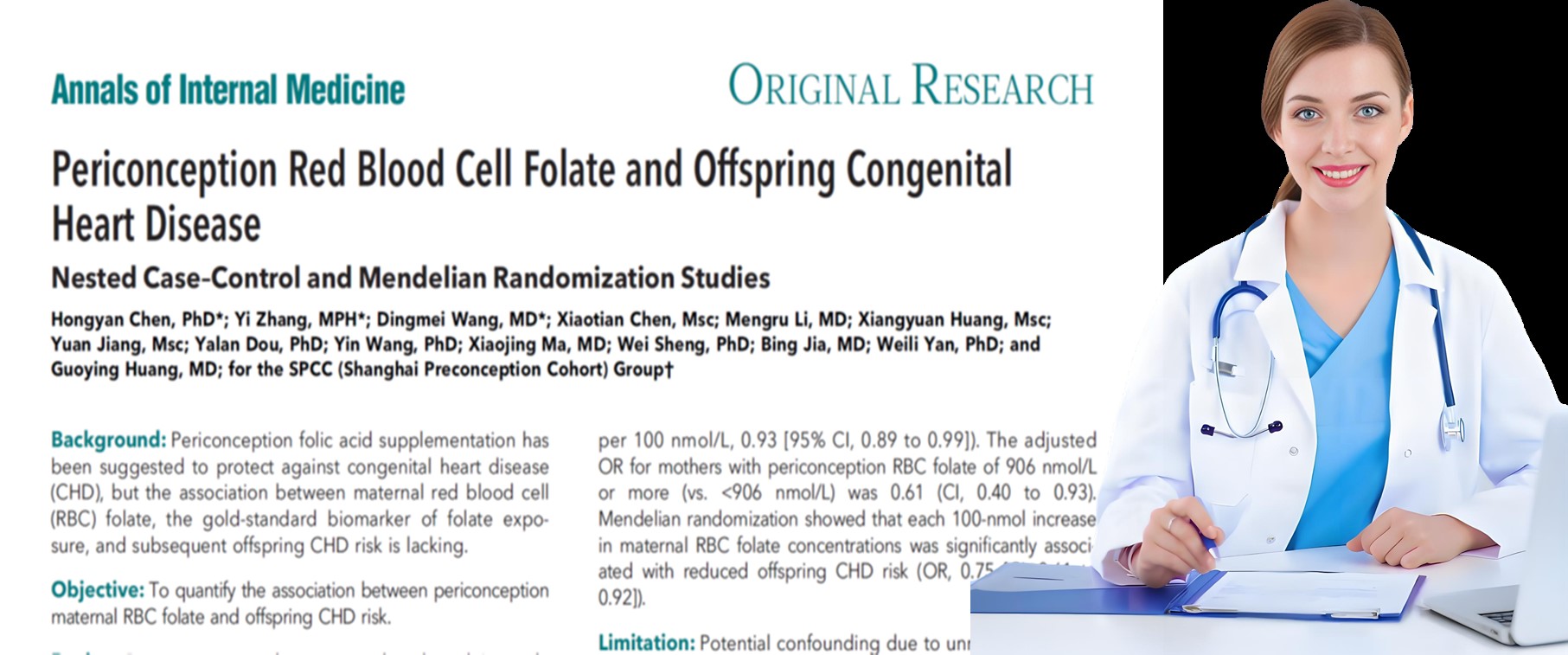
Yet, statistics reveal that a significant number of women planning pregnancy have low RBC folate levels. For instance, in Shanghai, over 90% of women preparing for pregnancy have RBC folate levels below the recommended threshold of 906 nmol/L for preventing neural tube defects.
Thus, supplementing folate to increase RBC folate levels during the periconceptional period is of utmost importance.
Limitations of Synthetic Folic Acid Supplementation
Currently, most pregnant women take synthetic folic acid. However, this form of folate has certain limitations. First, synthetic folic acid must undergo metabolic conversion in the body to become active. Yet, a large proportion of the population (78.4% in China have MTHFR gene metabolic disorders) has weak metabolic capabilities, leading to poor folic acid absorption.
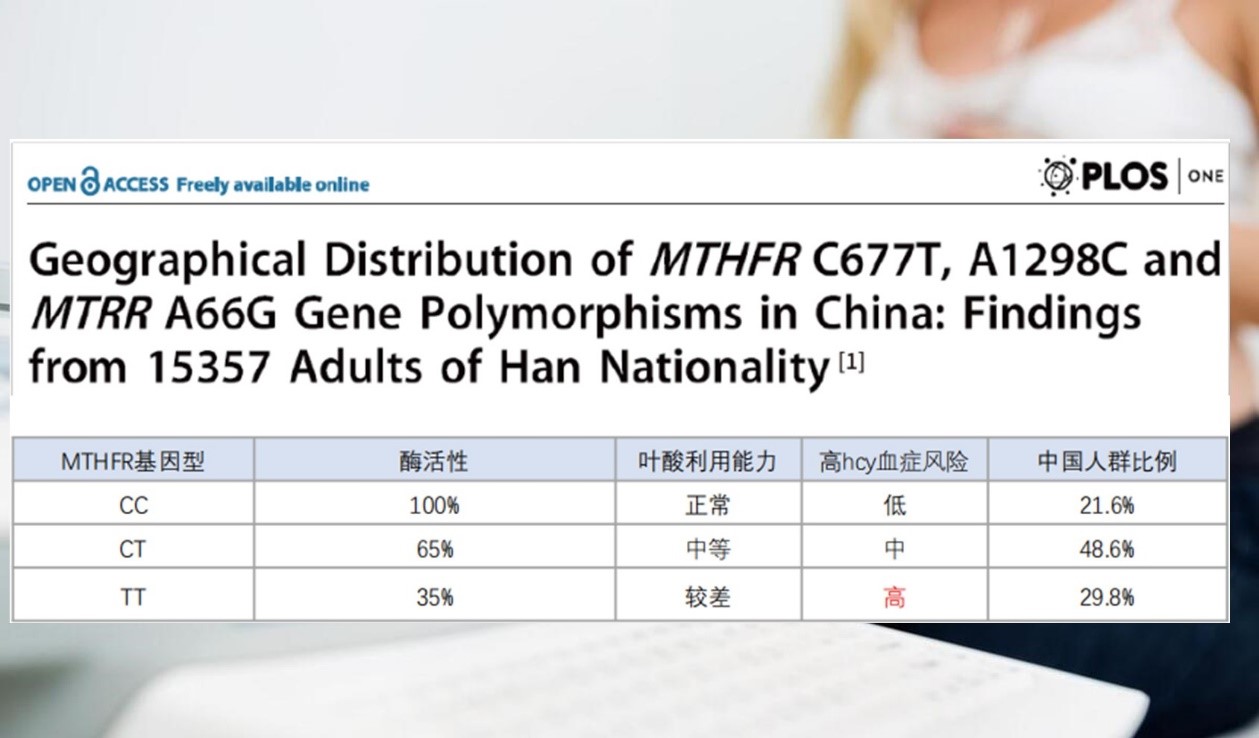
Second, high - dose synthetic folic acid may adversely affect the embryonic cardiovascular system, potentially increasing the risk of congenital heart disease.
Advantages of Naturalized Folate (L-5-MTHF-Ca)
Naturalized folate (L-5-MTHF-Ca) is the active form of folate that can be directly absorbed by the body without metabolism, unaffected by gene mutations. It offers higher bioavailability and safety and can rapidly increase RBC folate levels.

Additionally, experiments have demonstrated the good safety profile of L-5-MTHF-Ca, which does not pose any adverse effects on the embryonic cardiovascular system.
Research Findings and Practical Applications
It was found that after supplementing with naturalized folate (L-5-MTHF-Ca, trade name: Mag-nafolate), there was a significant increase in RBC folate concentration.
Research indicated that after 8 weeks of supplementation with naturalized folate (L-5-MTHF-Ca, Mag-nafolate), the RBC folate concentration in pregnant women rose remarkably from 283.026±219.578 nmol/L before supplementation to 780.244±221.878 nmol/L after 2 months, a 1.76 - fold increase, showing significant improvement.
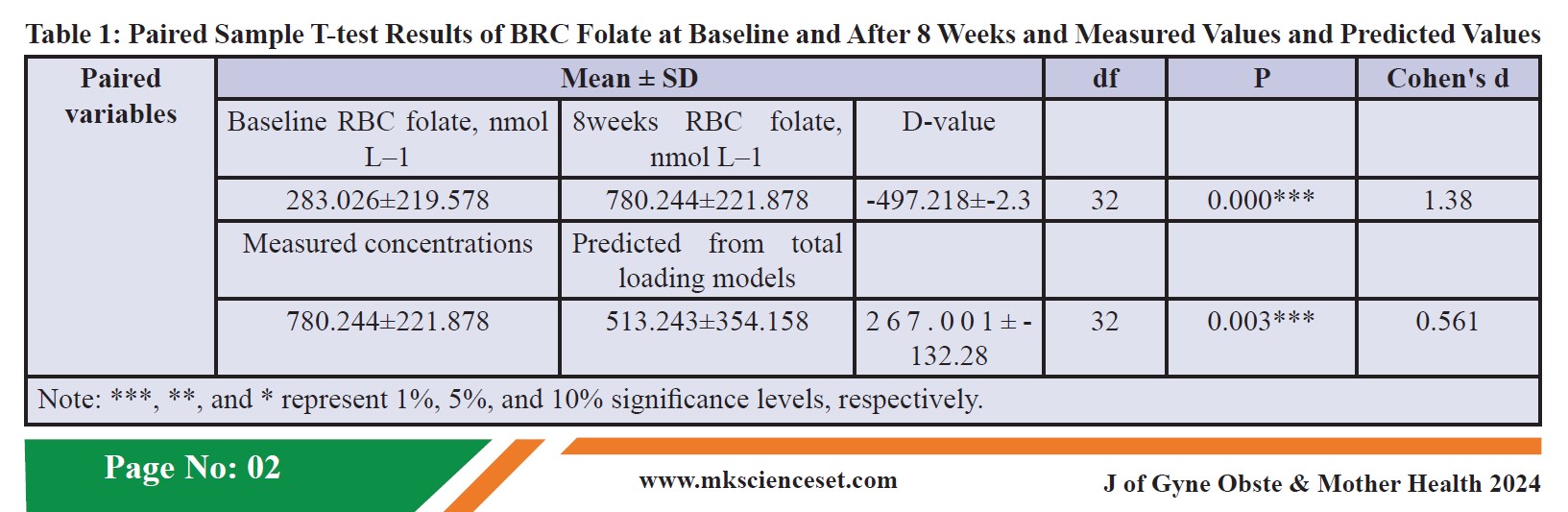
This suggests that naturalized folate (L-5-MTHF-Ca) can effectively address RBC folate deficiency and reduce the risk of birth defects such as neural tube defects and congenital heart diseases.
How Expectant Mothers Can Choose Folate Supplements
Faced with a variety of folate products on the market, how can expectant mothers make informed choices?

Personalized Supplementation: Pregnant or planning women should get MTHFR gene testing and check their RBC folate levels. Choose supplements with a doctor's advice. Normal serum folate levels alone can't show long-term deficiency risks.
Choosing Folate Products: If RBC folate levels are low (<906 nmol/L), prefer products with naturalization folate (L-5-MTHF-Ca), especially for those with MTHFR mutations.
Regular Monitoring: Test RBC folate levels every 2-3 months during pregnancy. Adjust the supplementation plan based on results to meet the recommended levels for preventing birth defects.
Future Research Directions
In the future, more multicenter, randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are needed to further verify the long - term safety and effectiveness of L-5-MTHF-Ca in different populations, such as those with MTHFR gene mutations.

Additionally, research should explore the synergistic effects of L-5-MTHF-Ca with other nutrients (e.g., vitamin B12) to provide more precise guidance for prenatal nutrition management.
Summary
Naturalized folate (L-5-MTHF-Ca) offers a new approach and option for folate supplementation during pregnancy. Expectant mothers should choose folate supplements based on their individual circumstances and doctors' advice, and work together to safeguard the health of both mother and baby.

Reference:Gu, R., Qi, D. (2024). Rapid Improvement with Crystal Form C of L-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate Calcium Salt in Maternal Women with Folate Deficiency: A Pilot Study, J of Gyne Obste & Mother Health, 2(6), 01-04.
 Español
Español Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türkçe
Türkçe  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  العربية
العربية  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan  Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski  मराठी
मराठी  Srpski језик
Srpski језик 








 Online Service
Online Service