At 26 weeks pregnant, Emily walked into the emergency room, leaning on her husband.
Her blood pressure was 160/110 mmHg, and her urine test showed protein +2.
Looking at the lab report, the doctor said with concern:
“Gestational hypertension. We
need to monitor closely for preterm delivery risk.”

This scene is not uncommon in obstetrics. In China, gestational hypertension occurs in about 5.22% to 5.57% of pregnancies.
A 2005 case-control study published in Epidemiology revealed a hidden risk behind “common knowledge”:

A functional mutation in the
MTHFR gene at position C677T—key to folate metabolism—significantly increases
the risk of gestational hypertension.
This 7-year study (1993–2000), conducted in Boston, Philadelphia, and Toronto, found:
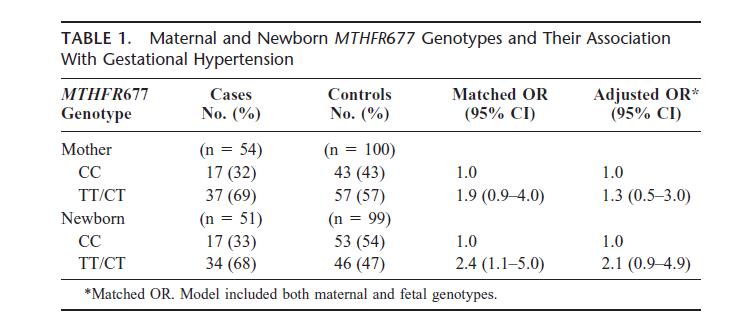
- · If the mother carries the 677T variant: Risk of hypertension ≈ 1.9× that of normal genotype.
- · If the baby carries the 677T variant: Mother's risk ≈ 2.4×.
-
· If both mother and baby carry the 677T variant: Risk ≈ 3× — the highest-risk combination.
MTHFR 677 is a key enzyme in folate metabolism. It helps convert synthetic folic acid into 6S-5-methyltetrahydrofolate — the bioactive form of folate that the body can directly use.

Insufficient 6S-5-methyltetrahydrofolate leads to elevated homocysteine (Hcy) levels, which damage vascular endothelial cells
and increase the risk of gestational hypertension.
Active folate bypasses this mutation and directly reduces the risk.

Among all active folate forms, Magnafolate — a naturalized folate — stands out due to its high purity, stability, and practical non-toxicity. Magnafolate is directly bioavailable, not limited by folate metabolism genes, and quickly raises serum and red blood cell folate levels.

It directly participates in
Hcy metabolism, effectively lowering maternal Hcy levels and reducing the risk
of gestational hypertension.

If you're trying to conceive, pregnant, or know someone like Emily,
switching from folic acid to Magnafolate is like patching a genetic
bug.
It bypasses the mutation and
builds a safe
folate defense line — every dose counts.
【Disclaimer】
This article is for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for
medical advice.
Always consult your doctor
before taking any supplements during pregnancy, especially if you have chronic
conditions or are on medication.
Folate supplementation is not a treatment for hypertension.
If you experience symptoms
like high blood pressure, swelling, or headaches, seek medical attention
immediately.
【References】
[1] Hernández-Díaz S, Wu XF,
Hayes C, et al. Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase Polymorphisms and the
Risk of Gestational Hypertension. Epidemiology, 2005, 16(5): 628–634.
[2] Lian Z, Liu K, Gu J, Cheng
Y, et al. Biological
Characteristics and Applications of Folate and 5-Methyltetrahydrofolate. China Food Additives, 2022(2): 1–8.
 Español
Español Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türkçe
Türkçe  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  العربية
العربية  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan  Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski  मराठी
मराठी  Srpski језик
Srpski језик 








 Online Service
Online Service